Bunion
Overview
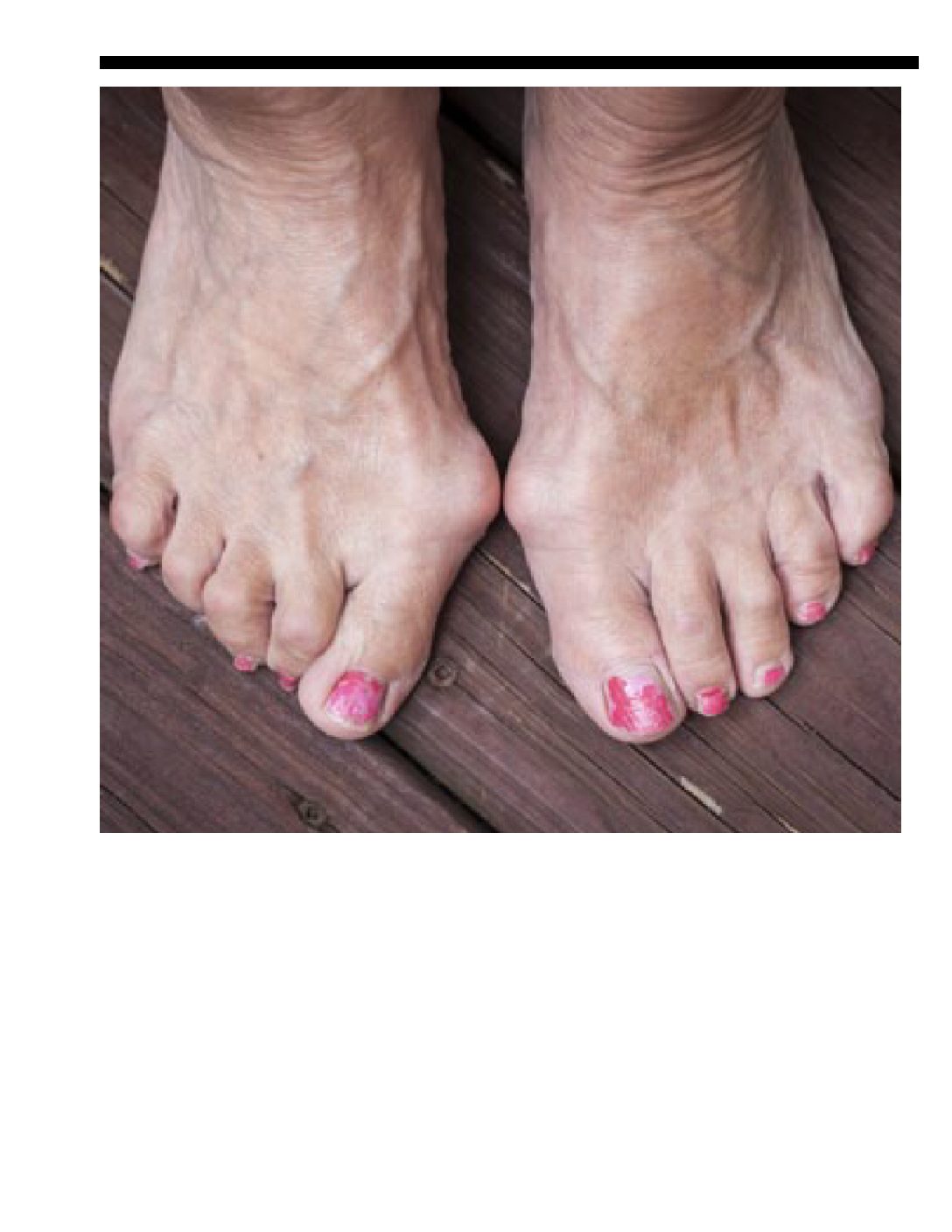
This deformity affects the joint at the base of the big
toe. It is a bony bump beneath the skin on the inner
side of the foot. A bunion starts small, but over time
it can grow to become very large. Bunions are more
common in women.
Causes
A bunion develops because of a pressure
imbalance in your foot. This imbalance makes your
toe joint unstable. The bones of your big toe begin
to shift and angle in toward your second toe.
Constant pressure causes the head of your
metatarsal (the bone at the base of your toe) to
become irritated. It gradually enlarges, forming a
bump.
Risk Factors
Wearing high heeled shoes, and wearing shoes
that are too tight or too narrow increases your risk
for developing bunions. Bunions have also been
linked to problems with the structure of your foot,
and to arthritis.
Symptoms
The most obvious symptom of a bunion is a visible
You may
experience pain, swelling and redness around the
affected joint. The skin may thicken. Your big toe
may angle inward. It may overlap or tuck under
your other toes. This can result in corns or calluses
Treatment
Treatment options depend on the severity of your
bunion. You may benefit from shoes that give your
toes more space. You may benefit from pads or
orthotic devices. You may benefit from medications
to control pain and swelling, and from applying ice
to your bunion. If these methods are not helpful, a
surgical procedure may be needed. Your
healthcare provider can create a care plan that is
right for your needs.