Type 2 Diabetes Explained
This disease is the most common form of diabetes.
With it, the hormone insulin has problems turning
blood glucose (commonly called blood sugar) into
energy. If untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to
many serious problems. Call the office about questions
concerning Diabetes and what is covered by your insurance.
Please call us at 509-443-5416.
Type 2 diabetes develops gradually. Normally, the
pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream to
help the body use glucose. But in some people, the
body develops a resistance to insulin. Glucose
builds up in the bloodstream. The pancreas
responds by releasing more insulin, but eventually it
cannot produce enough to meet the body's needs.
When this happens, the person has type 2
diabetes.
Many factors raise a person's risk for developing
type 2 diabetes. It most commonly develops in
people who are age 45 or older. People who are
overweight, physically inactive or who have family
members with this disease are at a higher risk. High
blood pressure, high cholesterol and vascular
problems raise a person's risk. It is more common
in certain racial and ethnic groups, including people
who are of black, Hispanic or Asian descent. And it
is more common in people who have developed
prediabetes, gestational diabetes or polycystic
ovary syndrome.
Symptoms may include increased thirst, increased
hunger, frequent urination and fatigue. The person
may experience weight loss and blurred vision.
Areas of darkened skin in the armpits and on the
neck may develop. The person may also have
sores that are slow to heal, and frequent infections.
However, some people don't notice any symptoms.
Diabetes can lead to a wide range of complications.
It can cause damage to the heart, the blood vessels
and the kidneys. Poor circulation can lead to
infections in the skin, especially in the feet.
Diabetes can lead to a type of nerve damage called
neuropathy. This causes numbness and tingling in
the extremities. Diabetes can lead to a loss of
vision and hearing. It can also increase the risk of
Alzheimer's disease.
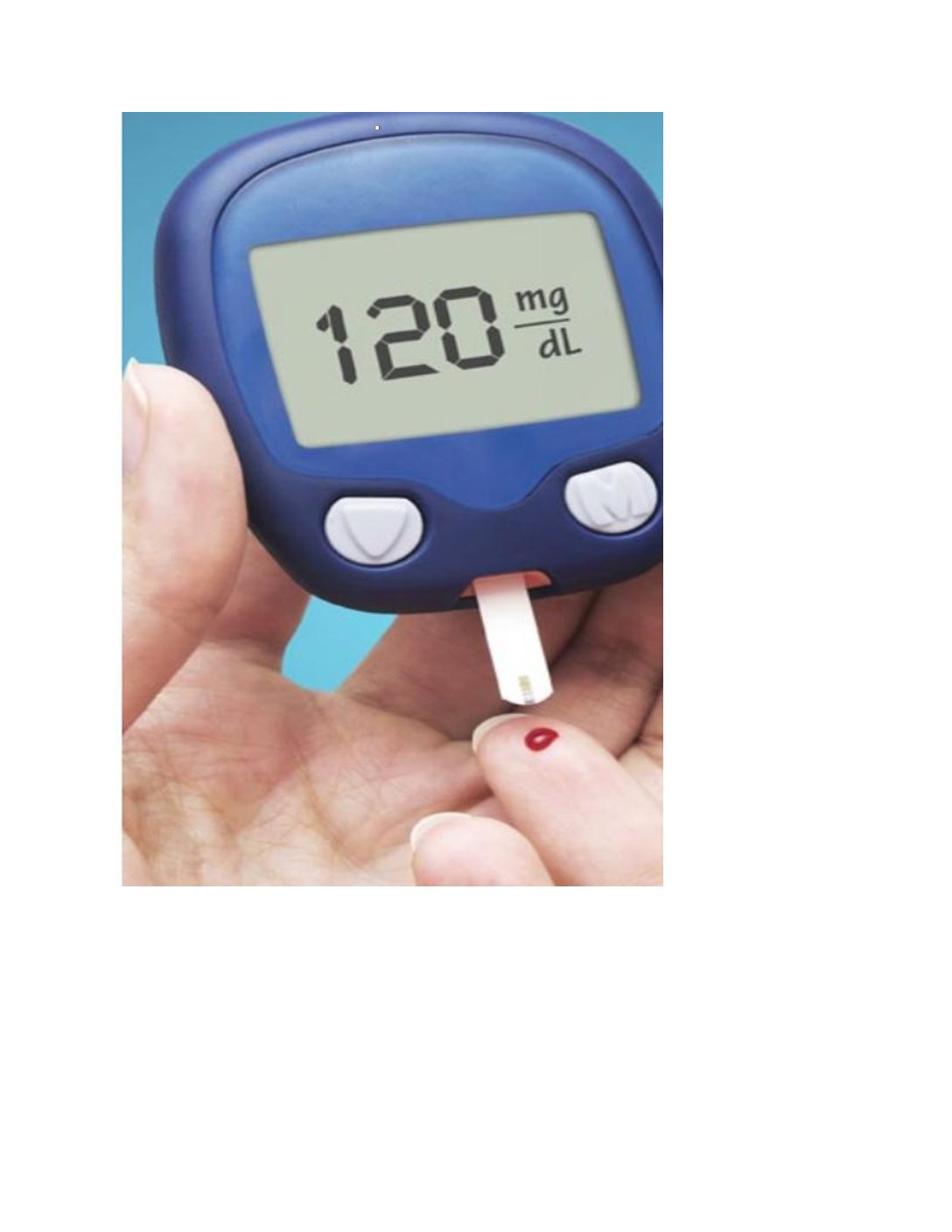
Type 2 diabetes can be managed with healthy
eating, regular exercise and careful glucose
monitoring. A doctor may prescribe medications to
treat diabetes or its complications, and insulin
therapy to help stabilize blood glucose levels